How Search Crawlers Organize Information and Index the Website?
The search engine acts as the answering machine. These search engines operate to organize the content in the best way and answer to what the searchers asked in their pages. For your website to appear among the search results, it needs first to appear to the search engines. If it doesn’t appear on their searches, then it is with no doubt that you can never occur within the Search Engine Result Pages. The search engine works under three primary roles to provide the best results.
Search engines have three main functionalities:
- Crawl – Search the Internet for quality content, viewing over the content for each of the link URL they find.
- Index – Save and arrange the content found. Once the crawling process for the searched page is in the index, it’s displayed as a result of a relevant query.
- Rank – Hover over the search engine database and provide the best result of the search query that will answer as ordered for the searcher’s query.
These three functionalities are described in details given as under:
Crawl
The Internet is involved in looking over for the URL within the content. They can also decide to look for the codes to get the perfect information. In this discovery process, the search engine takes part in sending out the crawlers, which are also termed as the robots, to get the most current content. They start to buy information from the web pages. They then use the links found on the webpages to get to the URL. Through the search, they can get the newly updated content and then add it to their index. The information is later retrieved when a search finds it to be best for whatever they are seeking.
Index
Once the content is found, it will be put in the list of the visited pages, and it is organized most appropriately. The content found during the crawling is stored and managed. The index is held to be displayed as an answer to the searchers’ already asked queries. All the content researched by the crawlers is stored within the indexing is then released when the searches find it useful for them.
Rank
The above two activities are behind the scene, but the result is put and most evidently shown on the web pages.
The search engine provides the very best answer from the different searches that will answer the asked query. Your query results are shown after the search engine indexes the page; it is displayed on the SERP.
The most relevant answer is prioritized. The ordering of the content which is more relevant to the query is the ranking. The contents are compared among the ones stored at the index page. For your content to be ranked, it should be accessible to crawlers, and it is indexable.
Crawling Process
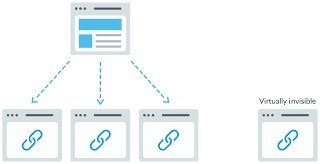
Website optimization make your website easily accessible for crawlers to identify it. They help you check your indexed page to ensure it has a domain name. Advanced search operators use this tool to see if the webpage has the domain name. With the domain name, you can retrieve the number of times that Google displayed the search results. To monitor this, Google search console results can be used, which gives a good result and report in the index coverage report. With the console tool, you can monitor the submitted pages and the number of pages that are already displayed within the Google index. Various reasons accrue to your site not showing up within the search results.
- If your web page is new and the crawlers have not gone through it.
- Your site could be linked with other external websites making it not to appear among the search results.
- If the site is penalized for being a spam
- If some settings which are navigated on the website hinder the crawlers
Crawling helps the site pages identify your page.
Website optimization services are essential to direct Google bot to ensure that your website content gets crawled. It provides better control of whatever activity ends up within the index. For old contents that contain thin contents, robots.txt is used. They suggest on the sites that you don’t need for them to be crawled. It will help if you are always optimized for the crawl budget. It involves the average number of URLs that the Google bots crawl on your page before leaving. It applies to large sites that have several URLs in their web pages.
- Common mistakes that keep the crawlers away from seeing your site.
- Navigations that show more sites on your page than on the desktop.
- When you forget the link to your primary web pages through navigation, it may not be crawled.
- If the menu page navigations are not on the HTML.
- If the carrier shows unique navigation as compared to the visitors, the crawling is not necessitated.
Indexing
Search engine data interpretation and storage on pages.
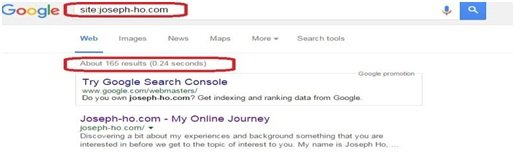
Once the website has been crawled, the next step is the indexing. The site’s pages of information and content are analyzed before it is indexed. Through the crawling, Google caches the webpage at different indexes. On scrawling your web page in the URL section, you can find the page’s cached visions.

It helps to determine if your page is visible enough for crawling. However, the pages can also be removed from the index. Reasons b being:
- If there is a case of an error in the URL page returning the indexing is not necessitated.
- If the metadata tab description is not available within the URL
- If the URL is blocked from crawling, indexing is not done.
- A penalized website from the search engines does not deserve to be indexed.
URL inspection tools are used to check the status of the page. It helps one identify in case of any issues that could be hindering the web page.
Website indexing
- Robots Meta directives
You can give directions on how you want your webpage to be indexed. One way is using meta directives. These directives mainly affect indexing and not crawling. You can give instructions in the search results for your page not to be indexed. Google bot crawls the pages to see the meta directives. The instructions can be executed from the Robots Meta Tag, accessible through the HTML web page.
The two types of robots meta directives:
1. The meta robots tag – a portion of the HTML page.
2. The X-robots-tag – those that the web server sends as HTTP headers.
Robots Meta Tag
Robots meta directives or meta tags are the bits of code that give to crawlers the instructions on how to index the web content. Whereas robot file directives grant Google bots suggestions on how to crawl a website’s pages, meta directives of robot file provide more directive instructions on indexing a page’s content.
Meta tags are accessible within the HTML of the webpage. Meta directives are available in Index/no index. It tells whether the page should be crawled and kept within the search engines or it should not.
Follow/Unfollow – It identifies the pages which should or should not be followed within the search engines.
X-Robot Tags
They are used within the HTTP header of the URL. It gives more description of the flexibility of the meta tags. The X Robots.txt file only contains crawler directives, by which search engines are instructed where they are or aren’t allowed to go.
Conclusions
A fantastic website that uses effective website optimization on effective crawling is essential in SEO success. You should always assure that you know the usage of the crawling and indexing. They are still important in avoiding some short comes that prevent essential pages from being seen. Practical strategies will even appear within the searches and attain high sales in the business.





